Avoid Overdraw in Your App
Overdraw in apps refers to a situation when the graphics processing unit (GPU) renders the same pixel multiple times due to overlapping UI elements. When your app's interface has overlapping layers with similar z-order (rendering priority), the GPU draws each layer in stacking order, even when other layers cover parts of elements (following painter's algorithm). This process wastes GPU resources by redrawing pixels that other elements cover, causing performance issues on resource-constrained devices.
Configure overdraw detection
To configure app overdraw detection, see Configure app launch options. In the project launch option, enter SHOW_OVERDRAWN=true. Then, run the app from Vega Studio.
How to interpret the overdraw results
The app shows overdraw with color indicators:
| Color | Overdraw level |
|---|---|
| Blue | GPU overdraws 1 time |
| Green | GPU overdraws 2 times |
| Pink | GPU overdraws 3 times |
| Red | GPU overdraws 4+ times |
How to reduce overdraw
After you identify overdraw areas in your app, use these optimization techniques to minimize GPU workload and improve rendering performance:
Flatten the view hierarchy
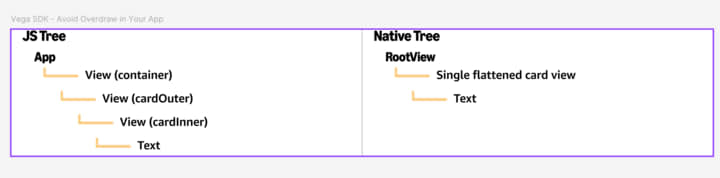
A flatter view hierarchy reduces overdraw for pure React Apps, but React Native's View Flattening Optimization can potentially flatten certain views to reduce the native component tree for you. The algorithm looks into backgroundColor, margin, padding or opacity style props to determine if it can flatten the view into a parent view.
In Javascript, your component tree hierarchy looks the same because React Native applies this optimization natively. Therefore, using tools such as React Dev Tools' component hierarchy viewer still shows the same hierarchy as your JS code. From the user’s perspective, there are no visible changes on the screen. By reducing the number of native view layers, this optimization minimizes overdraw where the GPU renders pixels multiple times due to overlapping views, resulting in improved rendering performance and smoother UI interactions.
// React Native flattens this code natively
import React from "react";
import { View, Text, StyleSheet } from "react-native";
export default function App() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<View style={styles.cardOuter}>
<View style={styles.cardInner}>
<Text style={styles.cardText}>React Native View Flattening Example</Text>
</View>
</View>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: "center",
alignItems: "center",
backgroundColor: "#f4f4f4",
},
cardOuter: {
padding: 12,
borderRadius: 8,
},
cardInner: {
padding: 16,
borderRadius: 8,
},
cardText: {
fontSize: 16,
color: "#333",
},
});
This diagram shows JavaScript view hierarchy compared to flattened native hierarchy.
Avoid transparency to reduce GPU workload
Transparent and semi-transparent views cause overdraw because the GPU must render all background layers before applying the transparency effect. However, there are scenarios when overdraw is expected. For example:
- Rendering a sidebar menu with a different background color than the rest of the app would experience overdraw
- Using semi-transparent layers to achieve your UI/UX.
When possible, you want to minimize large overdrawn portions of your app. Smaller areas like thumbnail-sized cards in a carousel are okay to have slight overdraw.
Best practices:
- Use opaque colors instead of transparent when possible.
- Avoid overuse of
backgroundColor. - Set one
backgroundColorat root level and avoidper-Viewbackground colors wherever possible. - Avoid stacking flat colors and/or semi-transparent layers (for example: background color grey, background color white, opacity, shadow).
Example:
// Avoid this:
<View style={{ backgroundColor: 'rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.5)' }} />
// Prefer solid colors:
<View style={{ backgroundColor: 'red' }} />
In the example, 0.5 is the alpha (opacity) value in RGBA format. When transparent elements overlap, the GPU computes and renders each layer separately, causing extra drawing operations and performance issues. Transparency increases GPU workload further because the GPU must blend background content with foreground content, adding extra drawing operations and performance issues.
Optimize images
Large, unoptimized images increase overdraw by forcing the GPU to render more pixels than necessary. Optimize images to reduce rendering overhead.
-
Choose the appropriate image format for your use case:
- JPEG: Photos and complex images
- PNG: Images with transparency
- WebP: Better compression than JPEG/PNG
- SVG: Simple icons and graphics
- Use appropriate image size and resolution images to match display dimensions. If the image asset is unavailable in various sizes (thumbnail, poster, full-screen), explore resizing.
-
Use multiple resolutions for different screen densities:
- my-image.png (1x) for standard resolution
- my-image@2x.png for 2x resolution devices
- my-image@3x.png for 3x resolution devices
- Use percentage-based dimensions or resizeMode for responsive designs. This ensures images scale appropriately across different screen sizes.
-
Avoid using
resizeMode: stretchas it distorts images and causes rendering overhead. Use 'contain' or 'cover' to maintain aspect ratio.<Image style={{ width: 100, height: 100 }} source={{ uri: 'image.jpg' }} resizeMode="contain" /> - Combine multiple icons into one file to reduce the GPU workload.
Reduce offscreen content
Rendering content that isn't visible on screen wastes GPU resources and causes unnecessary overdraw. Virtualizing your app's component tree helps reduce offscreen content by efficiently managing which components exist in memory, even when they're not rendered on screen.
Use virtualized components:
Virtualized components reduce offscreen content by only rendering items visible on screen. Vega supports multiple performant virtualized list options, such as FlashList (v1 and v2), LegendList, Carousel, and other pure JS list components. Choose the appropriate virtualized list component for your use case.
Best practices:
- Choose the appropriate virtualized component for your use case.
- Avoid rendering large offscreen content areas.
- Implement lazy loading for content below the fold.
- Remove or defer rendering of hidden UI elements.
Visit the App Performance Best Practices for implementation details.
Optimize animations with transform properties
Avoid animating layout properties like height, width, or margin, which trigger expensive recalculations and increase overdraw. Instead, animate the transform properties (scale, rotate, translate) that run on the GPU and don't affect layout Use useNativeDriver: true to ensure animations run on the native thread:
// Instead of animating layout properties:
<Animated.View style={{ height: animatedHeight }}>
...
</Animated.View>
// Animate transform properties instead:
<Animated.View style={{ transform: [{ translateY: animatedTranslateY }] }}>
...
</Animated.View>
Summary
To avoid overdraw in your app, start by enabling overdraw detection to understand the problem. If you can’t fix what you can’t measure, focus on:
- Optimizing images and animations.
- Reducing unnecessary re-renders.
- Removing unnecessary wrappers.
- Using appropriate components like FlashList.
- Reducing GPU workload and rework.
Related topics
Last updated: Dec 12, 2025

