Vega Headless Tasks and Services
JavaScript (JS) can run in the background without a user interface (UI) in two ways: headless tasks and headless services. Tasks are one-time operations that run independently, while services allow ongoing interaction. For example, a task might fetch TV channel data and update the program guide without opening the app. Services handle functions like media playback - the UI can send commands (like play or pause) to the service while it manages media streaming and processing in a separate runtime. This approach keeps the main interface responsive by moving heavy processing to the background.
JS runtime for headless JS tasks and services
Headless JS tasks and services utilize Vega App Components in the background. App components add a secondary JS runtime (powered by Hermes) on top to enable JS code execution and allow you to listen to lifecycle events from your code. Each instance of a headless JS task and service has its own JavaScript runtime instance.
Supported modules in headless JS context
To maintain a small memory footprint, the headless runtime is a simplified version of the available user interface and supports only the modules listed in the following table.
| Module | Note |
|---|---|
| Logging | console.log |
| Networking | fetch |
| Timers | |
| Promise | |
| Platform | Use '@amazon-devices/react-native-kepler/Libraries/Utilities/Platform' to import. import Platform from '@amazon-devices/react-native-kepler/Libraries/Utilities/Platform'; |
| Performance | global.performance.now |
ComponentInstanceManager |
Use '@amazon-devices/react-native-kepler/Libraries/ComponentInstance/ComponentInstanceManager' to import. import { ComponentType, type IComponentInstance } from '@amazon-devices/react-native-kepler/Libraries/ComponentInstance/ComponentInstanceManager'; |
FileReader |
Use '@amazon-devices/react-native-kepler/Libraries/Blob/FileReader' to importimport FileReader from '@amazon-devices/react-native-kepler/Libraries/Blob/FileReader'; |
URLSearchParams |
Use '@amazon-devices/react-native-kepler/Libraries/Blob/URL' to importimport {URLSearchParams} from '@amazon-devices/react-native-kepler/Libraries/Blob/URL'; |
I18nManager |
Use '@amazon-devices/react-native-kepler/Libraries/ReactNative/I18nManager' to importimport {I18nManager} from '@amazon-devices/react-native-kepler/Libraries/ReactNative/I18nManager'; |
Supported React Native libraries in headless JS context
Since the headless JS runtime supports limited modules, it only supports a limited set of React Native libraries, listed in the following table.
| Library | Note |
|---|---|
@amazon-devices/react-native-kepler |
Only select modules are available in headless JS context, see the list above. Do not import from root @amazon-devices/react-native-kepler. |
@amazon-devices/headless-task-manager |
|
@amazon-devices/react-native-w3cmedia |
Only import modules using "@amazon-devices/react-native-w3cmedia/dist/headless". Only version 2.1.66 and up have this "headless" export. |
@amazon-devices/react-native-mmkv |
|
@amazon-devices/react-native-async-storage/async-storage |
See react-native-async-storage documentation |
@amazon-devices/kepler-subscription-entitlement |
|
@amazon-devices/kepler-media-account-login |
|
@amazon-devices/kepler-content-personalization |
|
@amazon-devices/kepler-epg-provider |
|
@amazon-devices/kepler-epg-sync-scheduler |
Using unsupported modules
Using any module or library not listed above results in runtime errors, like the following example. This error complains about the DeviceInfo module that isn't available in headless JS context.
E Volta:[KeplerScript-JavaScript] Invariant Violation: TurboModuleRegistry.getEnforcing(...): 'DeviceInfo' could not be found. Verify that a module by this name is registered in the native binary., js engine: hermes.
This error can appear even when you don't directly import the problematic module.
The error happens when:
- You use a module that imports the problematic module
- You try to use an unsupported library
- You import a module incorrectly
For instance, if you import @amazon-devices/react-native-w3cmedia directly instead of using its headless export when writing code for headless JS, you'll see this error.
import { VideoPlayer } from '@amazon-devices/react-native-w3cmedia/dist/headless'; // Correct
import { VideoPlayer } from '@amazon-devices/react-native-w3cmedia'; // Incorrect
The headless export of @amazon-devices/react-native-w3cmedia only includes modules that work safely in headless JS. If you skip this export, your code will try to load UI-related modules that depend on unsupported features like DeviceInfo from @amazon-devices/react-native-kepler, causing errors.
While we plan to add tools that detect unsupported modules during build time, for now, make sure you only use modules that Vega has approved for headless JavaScript.
Build headless JS tasks and services
To register your headless JS tasks and services, you need to do the following:
Step 1: Advertise your components in app's manifest (manifest.toml)
// manifest.toml
# Copyright (c) 2024 Amazon.com, Inc. or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
#
# PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. USE IS SUBJECT TO LICENSE TERMS.
#
schema-version = 1
[package]
title = "Demo for Headless JS Task and Service"
version = "1.0.0"
id = "com.yourcompany.headlessjsdemo"
[components]
[[components.interactive]]
id = "com.yourcompany.headlessjsdemo.main"
runtime-module = "/com.amazon.kepler.keplerscript.runtime.loader_2@IKeplerScript_2_0"
categories = ["com.amazon.category.main"]
# App is indicating that it has a headless JS task
[[components.task]]
id = "com.yourcompany.headlessjsdemo.task"
runtime-module = "/com.amazon.kepler.keplerscript.runtime.loader_2@IKeplerScript_2_0"
# App is indicating that it has a headless JS service
[[components.service]]
id = "com.yourcompany.headlessjsdemo.service"
runtime-module = "/com.amazon.kepler.keplerscript.runtime.loader_2@IKeplerScript_2_0"
launch-type = "singleton"
Variations in manifest files
Different headless JS tasks and services need different settings in manifest.toml file. For example:
- EPG Sync Task uses
"runtime-module = /com.amazon.kepler.headless.runtime.loader_2@IKeplerScript_2_0" - Headless JS playback uses
"runtime-module = /com.amazon.kepler.keplerscript.runtime.loader_2@IKeplerScript_2_0"
Process management also varies by use case:
- Headless JS playback runs in the same process as your UI
- EPG Sync Tasks run in a separate process
Always check the specific documentation for each feature you're implementing. Don't copy settings between different headless JS features, as small differences can cause major problems.
Step 2: Register entry points
To register entry points for tasks (using the doTask function) and services (using the onStartService and onStopService functions), we recommend that you create two separate files: task.js and service.js. Place the files alongside index.js, which registers the entry point for the UI using AppRegistry.registerComponent. You can use task.js and service.js files to register entry points for multiple headless JS tasks and services.
// task.js - Registers entry points for Headless JS task
import { HeadlessEntryPointRegistry } from "@amazon-devices/headless-task-manager";
// SampleHeadlessTask.ts implements `doTask`
import { doTaskSampleTask } from "./src/SampleHeadlessTask";
HeadlessEntryPointRegistry.registerHeadlessEntryPoint2("com.yourcompany.headlessjsdemo.task::doTask",
() => doTaskSampleTask);
// service.js - Registers entry points for Headless JS service
import {HeadlessEntryPointRegistry} from '@amazon-devices/headless-task-manager';
// SampleHeadlessService.ts implements `onStartSampleService` and `onStopSampleServie`
import {onStartSampleService, onStopSampleService} from './src/SampleHeadlessService';
HeadlessEntryPointRegistry.registerHeadlessEntryPoint(
'com.yourcompany.headlessjsdemo.service::onStartService',
() => onStartSampleService,
);
HeadlessEntryPointRegistry.registerHeadlessEntryPoint(
'com.yourcompany.headlessjsdemo.service::onStopService',
() => onStopSampleService,
);
When using react-native build-vega to build your app, the process automatically handles headless JS bundles. Place these files in your project root:
- task.js for headless tasks
- service.js for headless services
The build system finds these files and creates:
- task.hermes.bundle for tasks
- service.hermes.bundle for services
These bundles are automatically included in your app package (VPKG).
.js extension. If they are called task.ts or service.ts, the react-native build-vega command will not pick them up, resulting in the missing task.hermes.bundle or service.hermes.bundle from the app VPKG. This could lead to ANR (Application Not Responding) crashes or other runtime errors.
// package.json
"scripts": {
.
.
"build:release": "react-native build-vega --build-type Release",
"build:debug": "react-native build-vega --build-type Debug",
"build:app": "npm-run-all build:release build:debug",
.
},
If you don't use react-native build-vega, you'll need to manually:
- Generate Hermes bytecode bundles from your entry point files (
task.jsandservice.js) - Add these bundles to your app package (VPKG) yourself
Debug headless JS tasks and services
Logging
To debug your code in headless JS tasks/services, you can use console logs (console.log) and see them in device Logs
Run the following command from your device or simulator shell:
loggingctl log -f | grep -i "<your package name>\|KeplerScript-Native\|KeplerScript-JavaScript"
To limit the logs from getting trimmed, use the following commands from the device or simulator shell:
loggingctl config --set-rate all 60000
<reboot the device>
loggingctl config --set-rate all 60000 // run this again
Quick JS bundle updates without rebuild
Headless JS tasks and services can now fetch the updated JS bundle without having to rebuild and reinstall the app.
Headless JS tasks and services don't support Hot Reload or Fast Refresh, which allows changes to be visible without relaunching. Instead, you need to relaunch headless JS tasks and services to pull the updated JS bundle.
To use this feature, follow the steps below.
- Build your app (UI and headless JS components) in debug mode. Note: Line-by-line debugging, as with UI components, doesn't work with release builds.
- Install the app.
- Run the Metro server (
npm start) from the project root. - Set up reverse port forwarding from your device (
target) to your development machine (host) for the port that the app and Metro are configured to use (typically8081). Without this step, the app can't connect to the Metro server.vega device start-port-forwarding --device <DEVICE_NAME> -p 8081 --forward false - Launch the app. You should see that all JS bundles (both UI and Headless JS) are now served by Metro.
Line-by-line Debugging
You can debug headless JS tasks and services line-by-line, but with some limitations:
- Only works with Vega Studio's Dev Tools
- Dev Tools only shows the most recently launched JS component
For example, in the Headless JS Media Playback app:
- Both UI and service run together
- The service launches last, so Dev Tools shows service.bundle
- To debug the UI instead, you must:
- Launch the headless service first using
vega device launch-app -a <Headless JS component name> - Then launch the UI component
- Dev Tools now shows index.bundle
- Launch the headless service first using
Follow these steps to use line-by-line debugging.
- Build your app (UI and headless JS components) in debug mode. Note: Line-by-line debugging, as with UI components, doesn't work with release builds.
- Install the app.
- Run the Metro server (
npm start) from the project root. - Set up reverse port forwarding from your device (
target) to your development machine (host) for port 8081 (or the port configured for your app and Metro). Without this step, the app can't connect to the Metro server and interact with the Dev Tools.vega device start-port-forwarding --device <DEVICE_NAME> -p 8081 --forward false - Launch the Headless JS task or service that you want to debug.
- Manually launch with this command:
kepler device launch-app -a <Headless JS component name>. - Launch the UI component.
- Manually launch with this command:
- In Vega Studio, open the Command Palette and choose "Vega: Launch Dev Tools". Navigate to the "Sources" tab and select "React Native".
- Verify that the listed bundle (
index.bundle/service.bundle/task.bundle) is the one you want to debug and that its source is loaded. Note: Dev Tools will display an error about failing to load the Source Map - this can be ignored. - To set breakpoints, search for your target code and click on the line number where you want to add the breakpoint. Note that breakpoints will only be hit for code that executes after the breakpoint is set. This means breakpoints in code that executes immediately upon launch (such as
doTaskfor headless JS tasks oronStartServicefor services) won't be triggered. For these cases, continue using logs for debugging. - Close the Dev Tools instance and relaunch it between app launches, as Dev Tools won't refresh automatically.
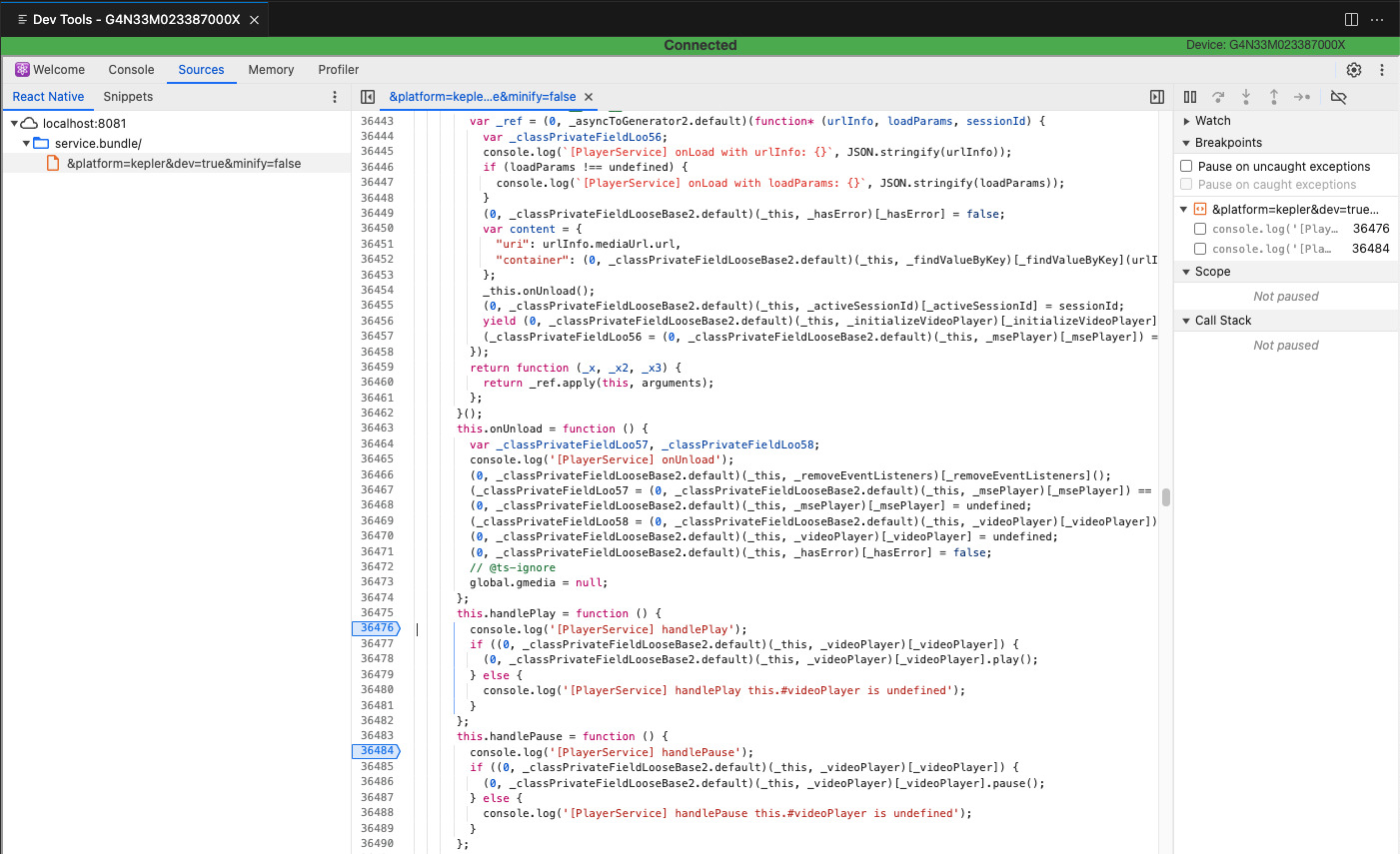
Crash Reports
Unhandled JS errors from a headless JS task or service cause the app to crash and generate an Aggregated Crash Report (ACR). Currently, this behavior only applies to release builds of headless JS tasks and services. For debug builds of headless JS tasks and services, continue to use Device Logs to detect any unhandled JS exceptions.
Troubleshooting issues with headless JS tasks and services
My headless JS task/services work in debug mode but doesn't launch or errors out in release mode
Check the logs and if you see an error like the following then your task/service bundle is trying to initialize or use a module that's not supported in headless JS context.
E Volta:[KeplerScript-JavaScript] Invariant Violation: TurboModuleRegistry.getEnforcing(...): 'DeviceInfo' could not be found. Verify that a module by this name is registered in the native binary., js engine: hermes.
To identify if that's the case you can do the following:
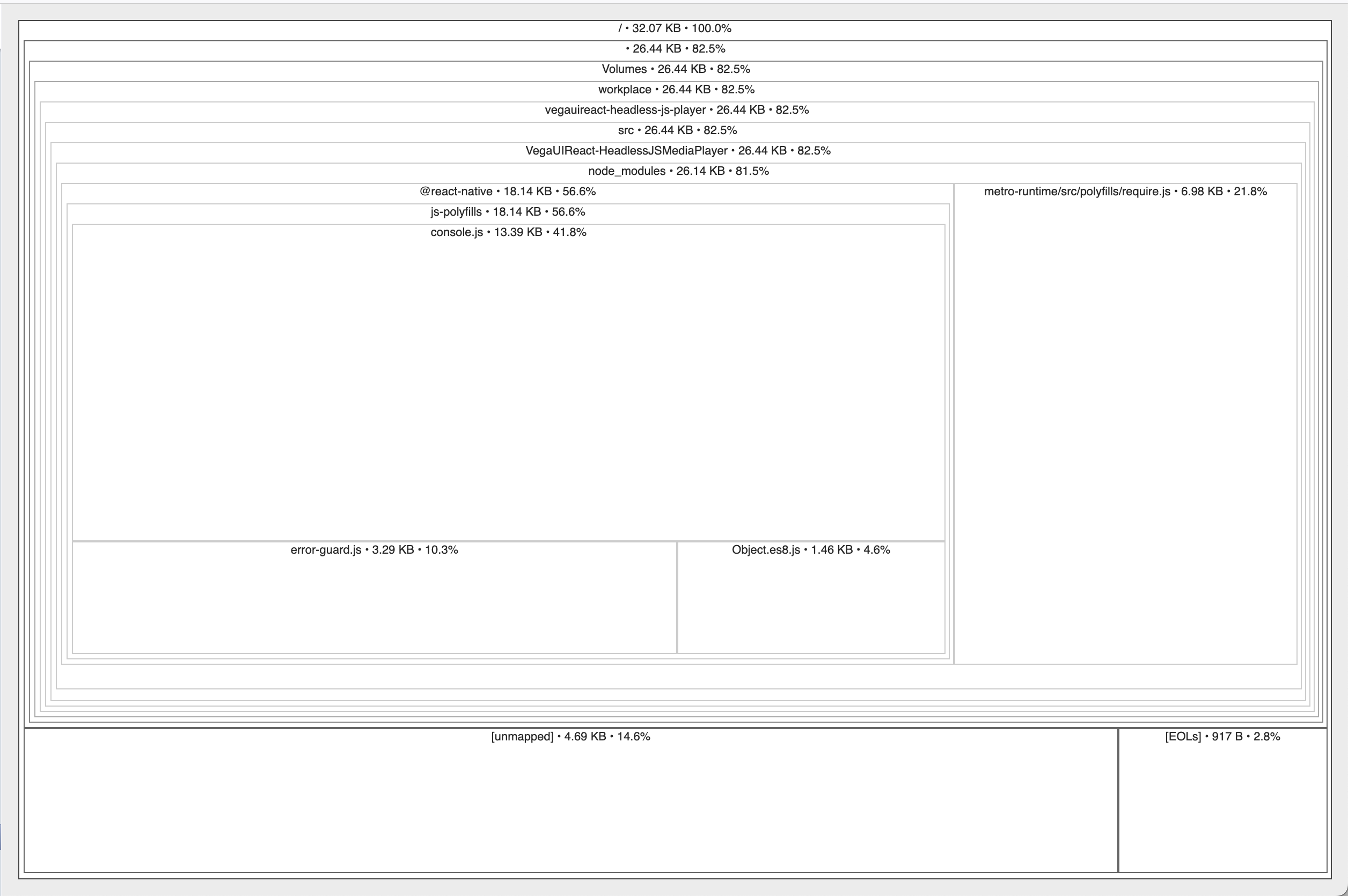
Step 1: Use react-native-bundle-visualizer to look at the composition of your headless JS task/service bundle
For example, compare the composition of a task.bundle when it accidentally pulls in the unsupported modules from @amazon-devices/react-native-kepler.
npx react-native-bundle-visualizer --entry-file task.js
Scenario 1: Correct import
// task.js
// correct import
import { ComponentType } from '@amazon-devices/react-native-kepler/Libraries/ComponentInstance/ComponentInstanceManager';
const componentInstance = {
name: "TestComponent",
type: ComponentType.TASK,
id: "test-123"
};
// Logging with enum value to string conversion
console.log(`Headless Task Test: Component Type: ${ComponentType[componentInstance.type]}`);
Scenario 2: Wrong import
// task.js
// wrong import
import { ComponentType } from '@amazon-devices/react-native-kepler';
const componentInstance = {
name: "TestComponent",
type: ComponentType.TASK,
id: "test-123"
};
// Logging with enum value to string conversion
console.log(`Headless Task Test: Component Type: ${ComponentType[componentInstance.type]}`);
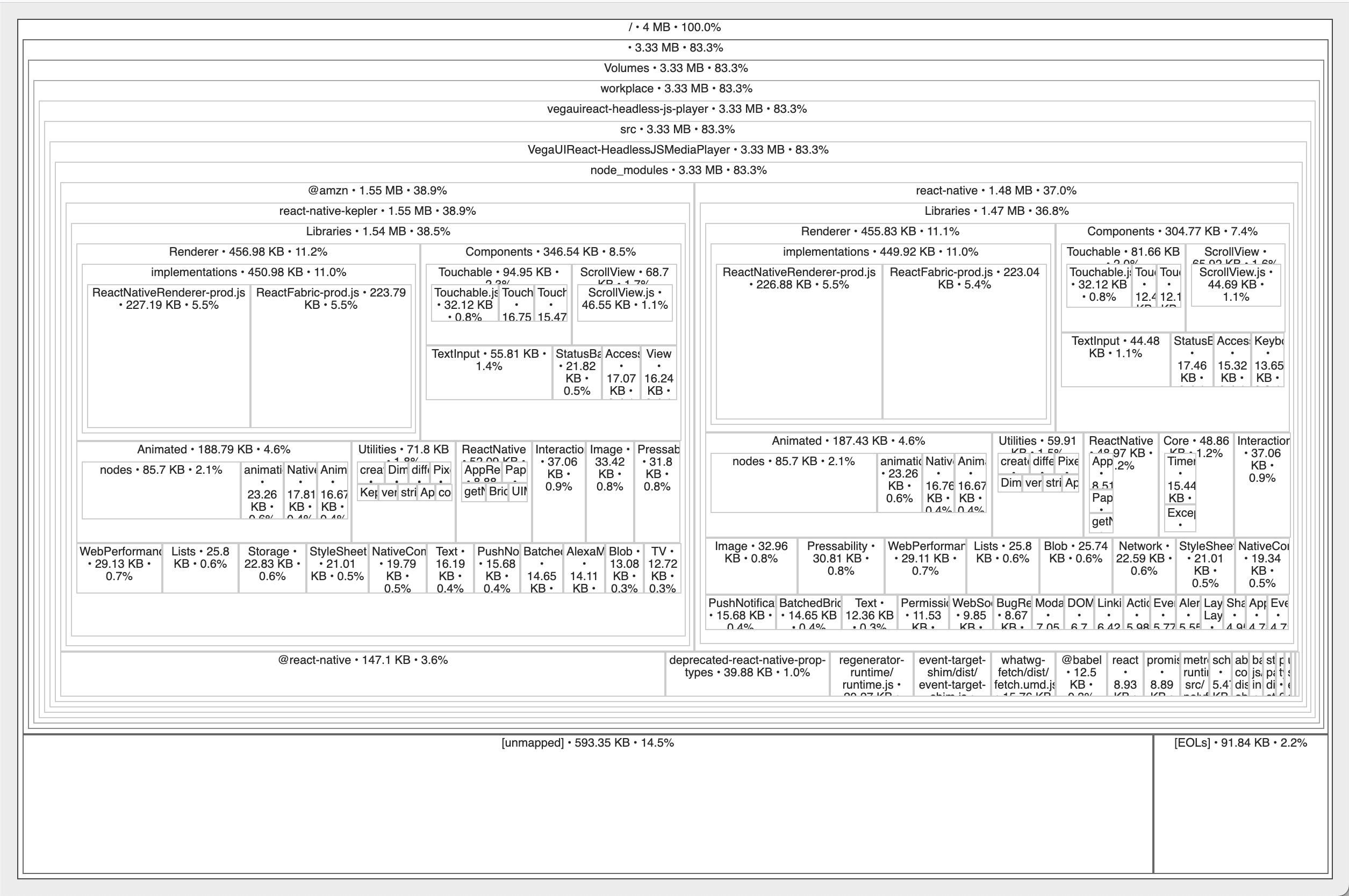
The composition of the task.bundle in Scenario 2 indicates that the bundle has included numerous modules from @amazon-devices/react-native-kepler, even those that are not supported in a headless JS context. Once you have confirmed that the task/service bundle includes unsupported modules, proceed to step 2 to determine who is responsible for bringing them in.
Step 2: Inspect the debug built task.bundle/service.bundle manually
Open the JS bundle (not the Hermes bytecode bundle) for the service/task (whichever is throwing error). You can typically find them in build/lib/rn-bundles/Debug. Let's say it is task.bundle. You can open it using any of your favorite editors.
For example, let's take the above task.bundle with the wrong import, and the following error:
E Volta:[KeplerScript-JavaScript] Invariant Violation: TurboModuleRegistry.getEnforcing(...): 'DeviceInfo' could not be found. Verify that a module by this name is registered in the native binary., js engine: hermes.
You can search for TurboModuleRegistry.getEnforcing call that takes DeviceInfo as the input.
Once you find that, you can determine which module has this code.
For example, in above task.bundle it is:
var NativeModule = TurboModuleRegistry.getEnforcing('DeviceInfo');
var constants = null;
var NativeDeviceInfo = {
getConstants: function getConstants() {
if (constants == null) {
constants = NativeModule.getConstants();
}
return constants;
},
// amznmod_react Use NativeDeviceInfo instead of RCTDeviceEventEmitter to add listener events
addListener: function addListener(eventName, handler) {
NativeModule.addListener(eventName, handler);
},
getDimensionsV2: function getDimensionsV2(rootTag) {
return NativeModule.getDimensionsV2(rootTag);
},
// amznmod_react Use NativeDeviceInfo instead of RCTDeviceEventEmitter to add listener events
addListenerV2: function addListenerV2(rootTag, eventName, callback) {
return NativeModule.addListenerV2(rootTag, eventName, callback);
}
};
var _default = exports.default = NativeDeviceInfo;
},247,[19,3,5],"node_modules/@amazon-devices/react-native-kepler/Libraries/Utilities/NativeDeviceInfo.js");
This code comes from @amazon-devices/react-native-kepler/Libraries/Utilities/NativeDeviceInfo.js.
Next step is to find out who is depending on this module. For that you can search for module ID 247 in task.bundle.
In the above task.bundle, there are two modules that depend on module ID 247:
},246,[3,12,13,4,5,247,20],"node_modules/@amazon-devices/react-native-kepler/Libraries/Utilities/Dimensions.js");
and
},564,[3,22,49,247,441],"node_modules/@amazon-devices/react-native-kepler/Libraries/Utilities/useVegaWindowDimensionsV2.js");
You can pick any one of these and search for its consumers. Doing this few more times leads to the following module: node_modules/@amazon-devices/react-native-kepler/index.js
},1,[2,471,481,484,485,378,20,487,395,490,491,493,494,498,500,28,478,472,404,271,324,408,457,503,288,505,507,418,482,483,421,511,512,513,232,514,515,516,521,171,523,526,375,528,222,199,531,534,444,535,537,455,188,246,337,45,267,334,538,540,364,365,436,82,174,152,151,542,544,245,546,548,550,551,553,259,31,555,556,19,35,446,558,559,563,564,565,568,569,98,570,572,573,4,575,182,21,17,207,204,274,441,296],"node_modules/@amazon-devices/react-native-kepler/index.js");
which is found to be imported from task.js
},0,[1],"task.js");
Future releases will automate the detection of offending modules using a tool. This tool could be integrated into the build step itself to warn about unsupported modules and their origin, potentially causing the build to fail.
Step 3: Reach out to your Amazon contact
If you've encountered a dead end due to the absence of a suitable tool to detect unsupported modules, Amazon will be more than willing to assist you in diagnosing the issue. Please reach out to your Amazon contact for the same.
Current applications of headless JS tasks and services
Headless JS tasks are employed for the following Fire TV integrations:
- Electronic Programming Guide
- Schedule work on app Install or Update: EPG Update, App Manifest Tasks
Headless JS Services are leveraged for the following use cases:
Last updated: Dec 10, 2025

